Microdeletion/Duplication Studies Using Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (For Research Only)
BACKGROUND:
Direct labeled probes which correspond to chromosomal regions deleted in a number of disorders can be applied to chromosomal spreads on slides prepared by routine cytogenetic techniques. Submicroscopic deletions, not visible by routine G-banding can be detected by this technique.
INDICATIONS FOR TESTING:
Testing is currently available for the following syndromes:
SYNDROME |
CHROMOSOME LOCATION |
PROBE/GENE LOCUS |
| 1p Deletion | 1p36 | LSIp58 |
| Wolf Hirschhorn | 4p16.1 | WHS |
| Cri-du-Chat | 5p15.2 | CDC |
| Williams | 7q11.23 | ELN |
| Angelman | 15q11-q13 | D15S10 |
| Prader-Willi | 15q11-q13 | SNRPN |
| Miller Dieker | 17p13.3 | L1S1 |
| Smith Magenis | 17p11.2 | SMS |
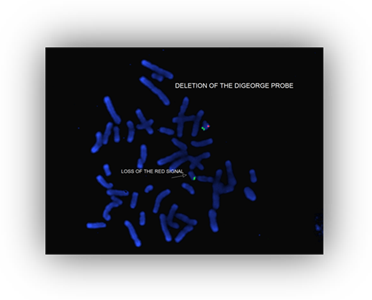
| DiGeorge | 22q11.2 | HIRA(TUPLE1) |
| Steroid Sulfatase, | Xp22.3 | STS |
| Kallman | Xp22.3 | KAL |
| Male Determining Factor | Yp11.3 | X/SRY |
SAMPLE REQUIREMENTS:
Five milliliters of whole blood collected by venipuncture into a green top sodium heparin tube. In newborns, 1-2 mls of blood may be sufficient.
SPECIMEN HANDLING:
Blood may be stored at room temperature overnight, refrigerated up to three days, but never frozen. Blood may also be mailed by overnight courier at ambient temperature. Blood drawn more than five days prior to receipt, or in the wrong tube (such as lithium heparin), is unacceptable.
PROCEDURE:
Slides are prepared in the routine manner and immediately placed at -20C until ready to use. Slides then undergo a series of dehydration and denaturation steps prior to hybridization with the probe. Hybridization generally occurs overnight in a warm humidified chamber. After a series of post washing procedures, the fluorescent signal is detected by amplification of the signal and counterstaining. The signal is then detected under a fluorescent microscope and digitized on a fluorescent imaging system.
INTERPRETATION:
Ten metaphase cells are generally counted and observed for the presence of the specific fluorescent signal. Deletions are detected by the consistent absence of the signal in one of the two homologous chromosomes.
RESULTS:
Generally, routine chromosomal analysis is performed in conjunction with FISH studies for microdeletions syndromes. The chromosome results are presented according to the international standards for chromosomal nomenclature (ISCN), and a full explanation of the karyotype and clinical implications is provided. A full description of hybridization studies is provided. Any abnormal or variant results are followed by genetic counseling.

 Institute of Genomic Medicine
Institute of Genomic Medicine